Hand and wrist pain can significantly impact daily life, hindering simple tasks and causing discomfort. From repetitive strain injuries to more severe conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, understanding the causes and treatment options is crucial for relief and recovery. Let's delve into hand and wrist pain treatment, exploring various modalities and interventions available.
Wrist pain is a common complaint arising from various causes, including injuries, medical conditions, and repetitive movements. Identifying the underlying source is essential for proper treatment.
Wrist pain can make everyday tasks challenging, but understanding its causes and treatment options can help you find relief. Various factors, from repetitive movements to sports injuries, can contribute to wrist pain.
Wrist pain can stem from various causes, affecting your ability to perform everyday duties comfortably. Common causes of wrist pain include:
Wrist injuries can cause significant discomfort. Not all wrist pain is due to injury; factors like repetitive movements and underlying medical conditions such as autoimmune diseases can also contribute.
To alleviate wrist pain, measures like applying ice packs to relieve swelling, using wrist splints for support, or seeking physical therapy to increase blood flow and flexibility can be helpful. Identifying the core cause of wrist pain is crucial for effective treatment, allowing individuals to find relief and resume their daily activities quickly.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve gets compressed due to irritation of the carpal tunnel. This tunnel is a narrow passage in the wrist that houses the nerve and tendons.
When the median nerve is compressed, it can cause symptoms like tingling sensation, numbness, or pain in the hand and wrist, particularly in the thumb, index, and middle fingers.
People with carpal tunnel syndrome may experience relief by wearing a wrist splint to keep the wrist in a neutral position or applying ice packs to decrease swelling and ease pain.
Severe cases may require medical intervention, such as corticosteroid injections or surgery, to relieve pressure on the median nerve. Risk factors for developing carpal tunnel syndrome include:
Repetitive hand movements.
Wrist injuries.
Certain medical diseases like psoriatic arthritis or autoimmune diseases.
Factors like pregnancy or obesity.
Seeking treatment early can help relieve symptoms and prevent further complications.
Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are autoimmune diseases that affect the joints, including wrists. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its tissues, particularly the synovium, which lines the joints.
This leads to inflammation, swelling, and pain in the affected joints. In the case of the wrists, rheumatoid arthritis can cause severe pain, stiffness, and difficulty with everyday duties.
Treatments like ice packs and medications may relieve pain and reduce swelling. Occupational therapists can also provide exercises and techniques to help manage symptoms and improve hand function.
Healthcare professionals typically begin with a thorough physical exam when assessing wrist conditions. During this exam, they examine your wrist for any signs of swelling, tenderness, or deformity.
They may also assess the wrist and surrounding joints’ range of motion and strength. Additionally, they’ll ask about symptoms such as pain, tingling, or numbness and inquire about any recent injuries or activities that may have contributed to the wrist problem.
This clinical evaluation helps provide valuable insight into the nature and severity of the wrist condition.

In some cases, further diagnostic tests may be necessary to diagnose wrist conditions accurately. One standard test is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the wrist and surrounding structures. This can help identify ligament tears, tendon damage, or bone abnormalities.
Blood tests may also be conducted to check for markers of inflammation or underlying medical conditions contributing to wrist pain.
These diagnostic tests complement the information gathered during the physical exam, providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying cause of the wrist condition.
By combining clinical evaluation with diagnostic tests, healthcare professionals can effectively diagnose and assess wrist conditions, allowing for appropriate treatment and management strategies to relieve pain and promote healing.
Wrist pain lasting a few days may indicate a minor injury or strain. When experiencing wrist pain, it's essential to seek proper treatment. This may involve:
Using wrist splints to ease discomfort
Applying an ice pack to relieve swelling
Taking anti-inflammatory medication to alleviate pain.
When wrist injuries are suspected, medical attention may be necessary to reveal bone fractures or ligament tears.
Non-surgical interventions offer effective alternatives for individuals seeking relief from wrist pain and related conditions without experiencing invasive procedures. For mild to moderate wrist pain, conservative treatments may suffice. These can include:
Total rest
Ice packs or cold compresses to relieve swelling
Over-the-counter pain relievers
Wrist splints to support and immobilize the joint
Stretching exercises to improve flexibility and reduce stiffness
Taking breaks from repetitive tasks can help alleviate strain on the small bones of the wrist. Wrist pain may gradually improve with proper rest and care over a few weeks.
Non-surgical interventions promote the body's natural healing processes and support wrist movement, ensuring optimal recovery without invasive treatments.
Physical and occupational therapy can also play a crucial role in relieving wrist pain by increasing blood flow, improving flexibility, and strengthening the muscles around the wrist joint.
By addressing persistent wrist pain and implementing appropriate treatment measures, individuals can regain mobility and comfort in their hands and wrists, allowing them to resume their daily activities quickly.
Various surgeries and medical management options are available to help reduce pain and improve function when treating wrist pain.
Procedures such as carpal tunnel release or wrist arthroscopy can help relieve pressure on the median nerve, repair ligament tears, or address underlying structural issues. If a wrist injury, such as a broken bone or damage to the connective tissue, is causing significant pain or limiting movement, surgery may be necessary to repair the damage.
Surgical procedures can range from fixing broken bones with pins or screws to repairing torn ligaments or tendons. In some cases, surgery may also be needed to remove ganglion cysts or alleviate pressure on a nerve, causing a tingling sensation.
Medical management options, such as pain medications, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physical therapy, can also play a significant role in treating wrist injuries.
For inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout, anti-inflammatory drugs or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and slow disease progression.
Physical therapist and hand therapist can provide exercises and techniques to improve wrist mobility and strength, while medications can help manage pain and inflammation. By combining surgical interventions with medical management, individuals can often achieve better outcomes and faster recovery from wrist injuries.
Hand therapy is vital in relieving wrist pain and promoting recovery from injuries. With a focus on improving mobility and function, hand therapists utilize various techniques to address issues related to the wrist bones and surrounding structures.
During therapy sessions, exercises are tailored to target specific areas affected by pain, aiming to strengthen muscles, increase flexibility, and improve overall wrist movement. Working closely with a hand therapist means individuals experiencing wrist pain due to common injuries or sports-related issues can expect to see improvements in weeks.
This therapy addresses the immediate discomfort and helps enhance the blood supply to the area, facilitating healing and reducing the risk of further injury. With consistent therapy sessions and guidance on proper techniques, individuals can regain confidence in their wrists’ abilities and quickly return to their daily activities.
Making ergonomic changes to your daily routine and work environment can help relieve wrist pain and prevent future discomfort. An occupational therapist can guide proper wrist positioning and techniques to reduce strain during repetitive duties.
Simple adjustments, such as using an ergonomic keyboard and mouse, maintaining proper posture, and taking regular breaks from activities that strain the wrists, can significantly prevent wrist pain from developing or worsening.
Additionally, ensuring that your workstation is set up correctly and supports wrists moving comfortably can help alleviate joint and muscle stress.
Managing risk factors associated with wrist pain is essential for maintaining wrist health and preventing injuries. For individuals with autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or underactive thyroid, it's crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to manage these conditions effectively.
Regular physical activity and a healthy lifestyle can also support overall joint health and reduce the risk of sports or repetitive strain injuries. By staying mindful of activities that may exacerbate wrist pain and taking proactive steps to address underlying health concerns, individuals can protect their wrists and enjoy greater comfort and mobility in the long term.
In cases of persistent or severe wrist pain, seeking evaluation and treatment from a specialist such as a hand surgeon, rheumatologist, or pain management physician is advisable. They can offer specialized care tailored to individual needs, ensuring proper diagnosis and treatment.
Participating in clinical trials or research studies may provide access to novel treatments or therapies for hand and wrist pain. These trials contribute to advancements in medical knowledge and may offer alternative options for individuals with challenging or refractory conditions.
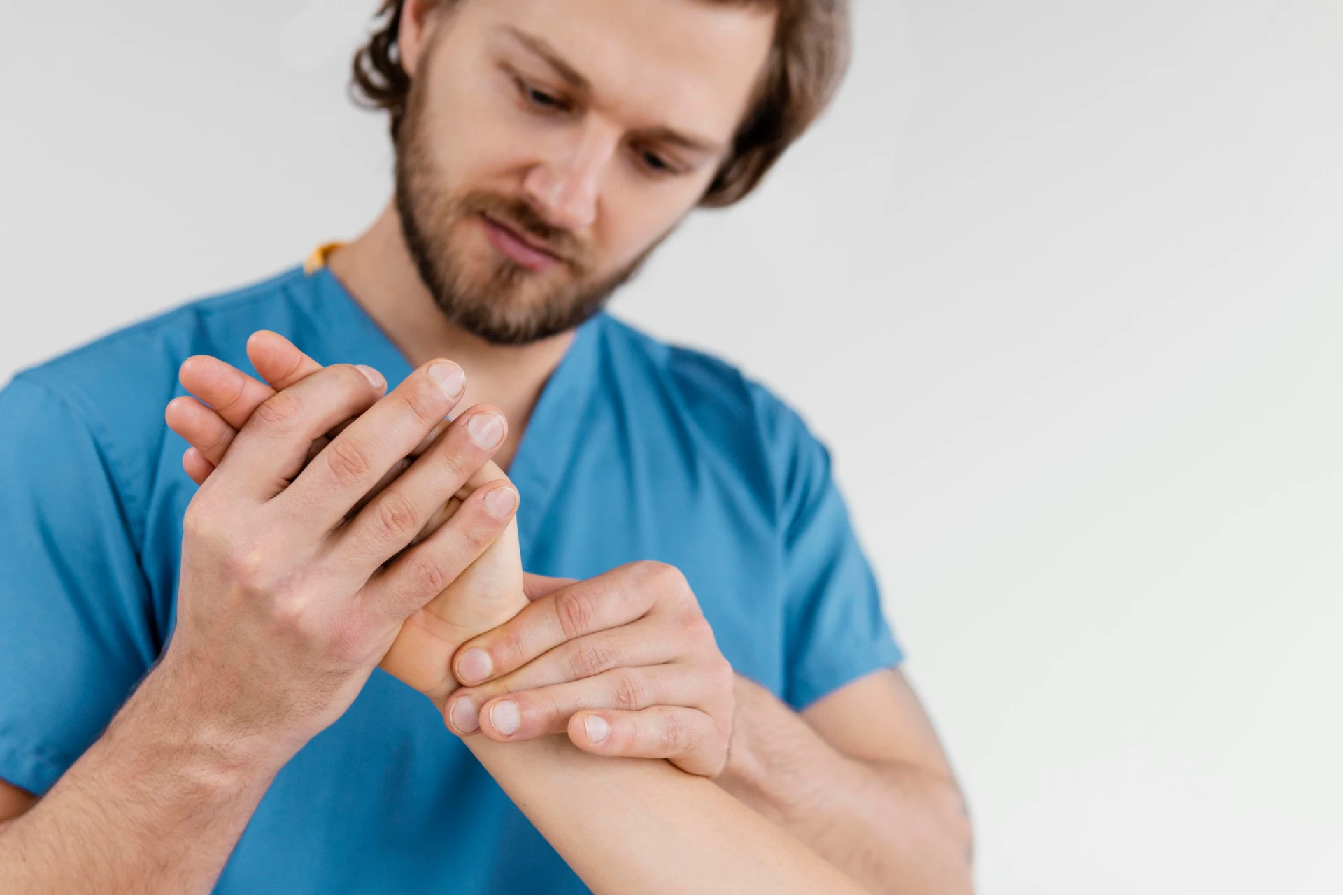
Hand and wrist pain treatment encompasses diverse modalities, from conservative measures to surgical interventions. By understanding the underlying causes, seeking proper diagnosis, and implementing appropriate treatment strategies, individuals can find relief and regain function in their hands and wrists. Whether through physical therapy, medication, surgery, or lifestyle modifications, addressing wrist pain promptly and effectively is essential for restoring comfort and mobility.
Located in Valley Stream and Brooklyn, we are committed to excellence by pledging to provide the highest quality of orthopaedic care possible.
© Copyright 2023 Advanced Orthopedics & Joint Preservation, PC. All Rights Reserved