Knee pain can seriously impact daily activities and quality of life. Understanding knee pain involves recognizing its various causes, which can range from acute injuries to chronic conditions. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to alleviate pain and improve function.
The lower leg plays a significant role in supporting the knee joint and absorbing shock during movement.
The knee, a complex joint connecting the thigh bone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia), is crucial for mobility and support. It comprises several components: bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
The femur’s rounded end rests on the flat upper surface of the tibia. Ligaments like the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) provide stability to the knee. At the same time, tendons such as the patellar tendon connect the quadriceps muscle to the shinbone.
Cartilage, like the meniscus, cushions between the bones, preventing friction and absorbing shock during movement. Knowing the knee’s anatomy is essential for spotting and dealing with problems to keep it working well and moving smoothly.
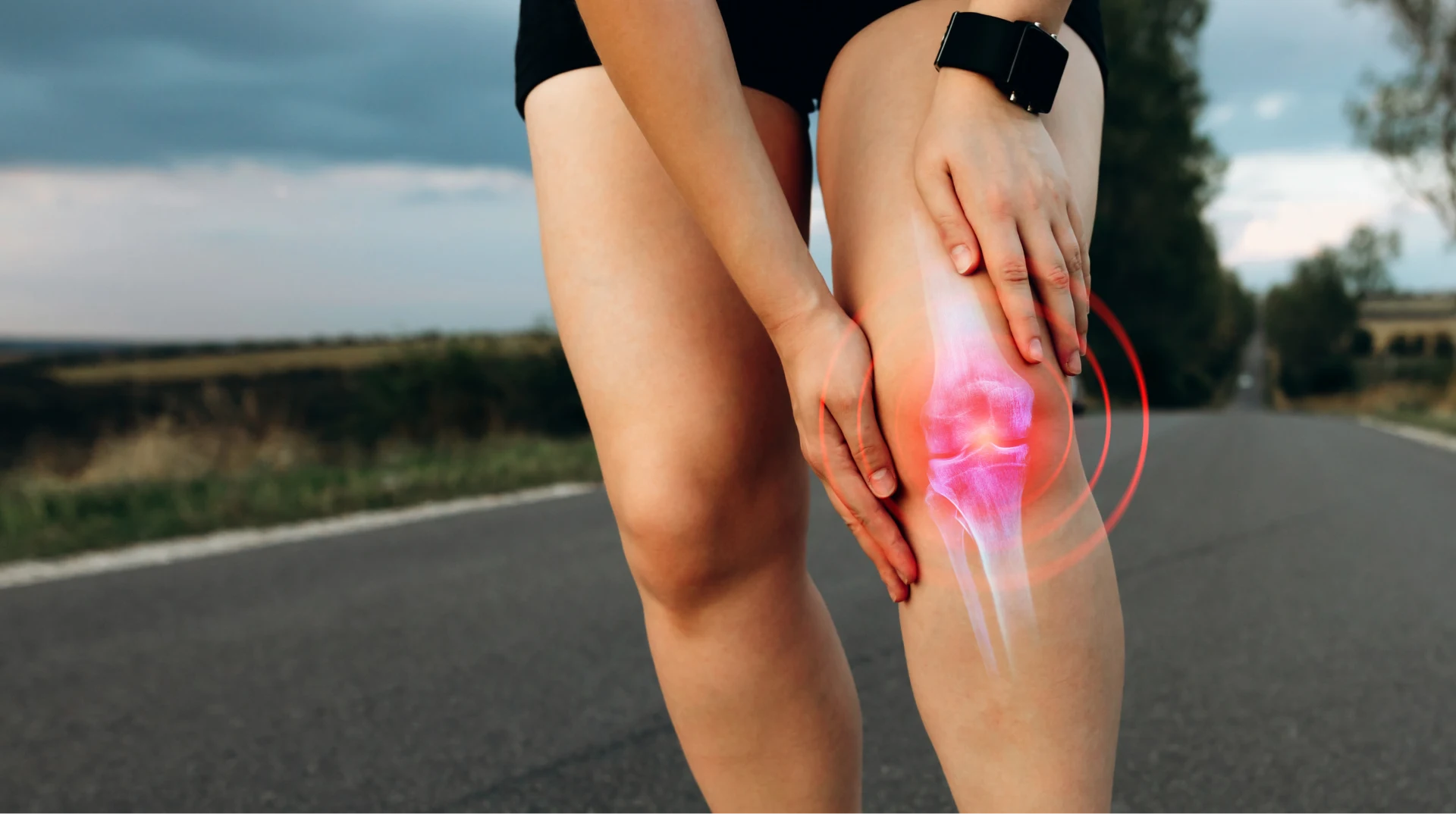
Knee pain can stem from various causes, from acute injuries to chronic conditions like arthritis. Common knee injuries, such as a torn meniscus or anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury, can result from accidents, sports activities, or repetitive motions.
Knee pain can be divided into four categories:
Injuries
Arthritis
Overuse
Other factors
If we talk about knee injuries, it might be:
Ligament tears (e.g., anterior cruciate ligament or ACL injury)
Dislocated kneecap
Torn meniscus
Patellar tendonitis
For conditions like mild arthritis or tendonitis, nonsurgical interventions like corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections may be recommended.
Arthritis pain can affect the knee. Usually, elderly individuals experience pain in the knee due to arthritis. The most common arthritis include:
Osteoarthritis: It occurs when the protective cartilage on the ends of the bones wears down over time, leading to pain, swelling, and decreased joint mobility.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: This is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. It can affect multiple joints, including the knees, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness.
Post-Traumatic Arthritis: This type of arthritis can develop after a knee injury, such as a fracture or dislocation. The damage to the joint surfaces may lead to the development of arthritis over time.
Gout: Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals build up in the joints, causing intense pain and inflammation. While it often affects the big toe, it can also impact the joint.
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or patellofemoral pain syndrome can lead to chronic knee pain. Many athletes experience knee pain after intense workouts. Even changes in weather conditions, such as cold temperatures, may cause some individuals to experience pain.
If your knee hurts consistently, seeking medical attention to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment is essential.
Repetitive activities or strain on the knee joint, such as in runner's knee or jumper's knee, can result in pain and discomfort.
Other factors that may cause knee pain are trauma from different situations, like car accident, broken bones, or conditions like iliotibial band syndrome, which can also contribute to knee pain.
Individuals with previous knee injuries may experience pain in the knee during certain activities.
There are various ways to treat knee pain, including therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications. Effective nonsurgical treatment for knee pain involves multifaceted methods tailored to address the underlying cause and alleviate symptoms.
Nonsurgical treatment for knee pain varies depending on the underlying cause, with options including:
Total rest for injured knee
Using an ice pack and compression bandage if needed
Over-the-counter drugs to relieve pain
In cases where knee pain is due to issues with knee cartilage or the patellar tendon, targeted physical therapy exercises can aid recovery and improve joint function. Elevating the affected knee and applying an ice pack can also help reduce inflammation and pain.
For severe cases or when conservative measures fail to provide relief, medical interventions like total knee replacement surgery may be necessary to restore mobility and alleviate chronic pain.
Overall, effective treatment for knee pain aims to alleviate discomfort, improve function, and enhance the quality of life for individuals experiencing knee issues.

When knee pain occurs, various strategies can provide relief and promote healing. Straight leg raises can strengthen the muscles and ease knee pain by reducing strain on the joint.
A customized physical therapy program helps patients regain strength, flexibility, and movement in the knee. It also helps reduce joint pain and swelling.
Joint pain relief methods may include gentle exercises, hot or cold therapy, and over-the-counter pain medications. The treatment typically begins with gentle exercises and stretches to improve mobility.
Keeping the knee elevated can help reduce swelling and discomfort. The goal of the therapy for knee injury is to:
Restore function of the knee
Improve overall knee health
Help individuals return to their normal activities with confidence and reduced risk of re-injury.
Adequate blood flow is essential for healing injured tissues, including ligaments and tendons in the knee. Elevating the knee can help reduce swelling and discomfort, especially after strenuous activity or injury.
To prevent knee pain and need fast relief to help, your doctor may prescribe you over-the-counter pain relievers or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This medicine can provide temporary relief from knee pain and inflammation.
Another way of pain management is RICE: Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). It is a standard approach for managing acute knee injuries, helping to reduce swelling and alleviate pain. To prevent further damage, pressure on the knee should be significantly avoided if it’s injured or painful.
Treating knee pain with knee braces provides support and stability for the knee joint, particularly during physical activity or sports. Wearing a knee brace can provide support and stability for injured or weak knees, aiding recovery and reducing discomfort.
When knee pain is severe and ongoing, surgery might be an option for lasting relief and better function. Possible surgical options for knee pain include:
Knee replacement surgery: The damaged parts of the knee joint are replaced with artificial components made of metal and plastic. This procedure is recommended for people with severe arthritis or significant joint damage.
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure. Arthroscopic surgery uses a small camera and instruments inserted into the knee. It helps diagnose and treat knee problems such as torn cartilage or damaged ligaments.
Lateral release or cartilage restoration: These techniques are performed for specific conditions like patellofemoral pain syndrome or torn cartilage.
Ultimately, the choice of surgical option depends on factors such as:
The severity of the knee injury
The individual’s overall health
The recommendations of the orthopedic surgeon
Individuals must discuss their treatment options thoroughly with their healthcare provider to determine the most suitable approach for managing knee pain and improving their quality of life.
To prevent knee pain, stay active with regular exercise to strengthen knee muscles and keep a healthy weight to ease pressure on the joint. Familiar and easy-to-provide measures include:
01
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can place additional stress on the knee joints, leading to pain and increased risk of injury.
Proper Technique: Doing it right can stop knee injuries when you exercise or play sports.
Strength Training: Strengthening leg muscles like the quadriceps and hamstrings can make your knee stronger and more stable.
Avoid Overuse: Resting between workouts and slowly making workouts harder can stop knee problems from happening.
Protective Gear: Wearing appropriate footwear and using protective equipment, such as knee pads for high-impact activities, can reduce the risk of injury.
Chronic knee pain can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Finding effective pain relief for knee discomfort can dramatically improve mobility and quality of life.
Knee health is crucial for mobility and comfort. Consultation with an orthopedic surgeon may be necessary for severe knee conditions.
Treating knee pain means finding out what’s wrong and using different methods to help. These methods can include exercises, medical reliever procedures, using a brace, and sometimes surgery.
To feel better and keep moving, it’s essential to deal with knee pain early and do things to prevent it. This can help reduce discomfort, make it easier to move around and keep your joints healthy so you can do more.
Located in Valley Stream and Brooklyn, we are committed to excellence by pledging to provide the highest quality of orthopaedic care possible.
© Copyright 2023 Advanced Orthopedics & Joint Preservation, PC. All Rights Reserved